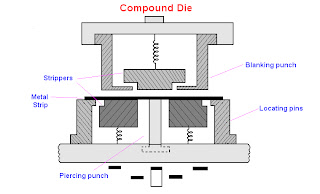
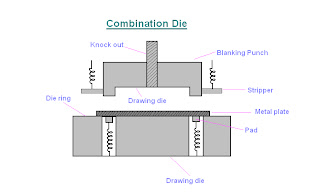
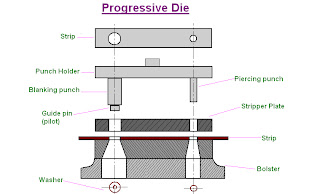
Aluminum casting process is not required to consider the following questions:
1) in the liquid metal in the filling system can clean, smooth flow, there is no vortex and.
2) there is no angular or dead?
3) if cross domain triggering system changes?
4)
The performance of paint coatings produced gas analysis: the air to
create porosity in aluminum castings have a direct impact. Projection
process: the excessive, leading to significant evaporation of gas, too
punch lubricant, or burns, are the source of gas.
5) The answer to the first aluminum casting porosity analyze the causes of pores again take appropriate action.
1) dry, clean alloy.
2) to control the melting temperature to prevent overheating and gas processing.
3) Melt a reasonable choice of process parameters, the extraordinary is the speed of injection. High speed switch for adjusting the starting point.
4)
The order of the high pressure sodium lamp filled with the help of gas
emissions, carrots and runner length sufficient to facilitate the free
flow of gas and liquid alloy has the ability to download. Can change the thickness of a door, address, forming pores in the position set for the overflow reservoir, the discharge ducts. Sectional
area of the overflow of the product can not be less than the sum of
the gate within 60% of the total cross-sectional area, or slagging poor
results.
5) Selection and control of spray paint with good volume. Ideas
to remedy the deficiencies that cause each fault from a number of
different factors, so that the actual production to solve the problem,
because in the face of many non-merits and demerits of the machine
first transfer? Or before refueling? Or modified before the mold? We propose that the degree of difficulty, after the first dealing with the complex simplicity,
The order:
1)
in the return surface, the cleaning of the cavity mandrel cleaning, the
improved coatings to improve the sputtering process, increase the
clamping force to increase the amount of molten metal. These operations can be implemented by simple measures.
2)
adjusting the process parameters of the injection force, injection
speed, fill time, the molding time, the casting temperature, mold
temperature. 3)
for materials, ingots select high quality aluminum alloy, the material
again and again to change the ratio of filler to improve the process of
fusion.
Cast aluminum produced flash of reasons:
1) Problem aluminum smelter: adjusts the clamping force not.
2) a technical problem: the injection speed is too high to form a peak pressure impact.
3)
mold problems nonstick cookware deformation, type of surface debris,
inserts, cursors used does not work, the model is not strong enough. Measures
to resolve the flashing sequence: surface clean separation to improve
the clamping force adjusting parameters of wear parts mold repairs to
improve the rigidity of the mold.